Reducing Sugar Disaccharides Examples. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. Here are some common examples of reducing sugars. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of benedict's or fehling solution to cuprous ions. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose.
Reducing Sugar Disaccharides Examples . In Basic Aqueous Media, Nonreducing Sugars Do Not Generate Any Compounds Containing An Aldehyde.
Qc Biochem371 Chap 7 Vocab And Question Flashcards Quizlet. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. Here are some common examples of reducing sugars. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides. In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of benedict's or fehling solution to cuprous ions. Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide.
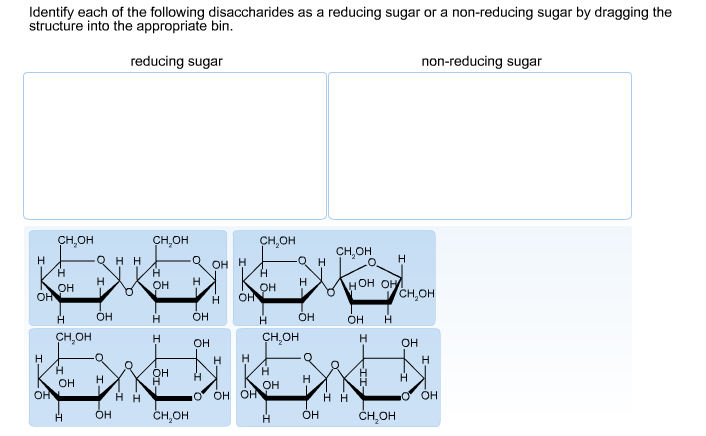
Reducing sugars aid in browning by reacting with proteins during baking.
These carbohydrates are represented and their formulas are. I fail to see carbonyl group here, how can i identify. The aldehyde functional group allows the sugar to act as a reducing agent, for example in the. Reducing sugars are essential ingredients in these reactions, providing the carbonyl groups for interaction with the free amino groups of amino acids, peptides, and proteins. The two tests indicate the present of. Examples of reducing disaccharides are lactose and maltose. ( d) examples of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. What are reducing sugars ?? The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Disaccharides are hydrolyzed to their constituent monosaccharides when boiled in dilute hydrochloric. Not all disaccharides will get positive results with this test. The properties of trehalose are the same as that of other disaccharides except the reducing power. In the instance of disaccharides, structures that. It's easy to identify them in monosaccharides but this becomes confusing in case of disaccharides! Note that the disaccharide sucrose is not a reducing sugar. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. To be a reducing sugar, you have to have either an aldehyde or a ketone functional group. Although the term sugar is commonly used to refer to sucrose, sucrose is only one in general, disaccharides and polysaccharides contain both reducing and nonreducing sugars. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. Sucrose, or table sugar, is the most common disaccharide. These carbohydrates are represented and their formulas are. Glucose and fructose are examples of reducing sugars. The initial rate of this reaction is dependent on the rate at which the sugar ring opens to the oxo or reducible form. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. I'm only going to talk about aldehydes, but it is the same for usually when a disaccharide forms (2 glucose units, for example), the bond that links them is between the hemiacetal of the first glucose and the 4. Therefore disaccharides like sucrose are not reducing sugar. This allows the sugar to act as a reducing agent, for example in the maillard reducing sugars (monosaccharides, e.g. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: Test for lowering sugars (benedict's test). Table sugar is an intermediate product of photosynthesis, composed of fructose and glucose, synthesized only by disaccharide composed of two molecules of glucose, appears during the hydrolysis of cellulose and is characterized by being reducing. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules.
Add Your Page Title . A Reducing Sugar Is Any Sugar That, In Basic Solution, Forms Some Aldehyde Or Ketone.
16 7 Disaccharides Chemistry Libretexts. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of benedict's or fehling solution to cuprous ions. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Here are some common examples of reducing sugars.
Lecture 24 - Pairs Of Monosaccharides Can Be Combined To Form A Disaccharide.
Maltose An Overview Sciencedirect Topics. In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars.
Reducing Non Reducing Sugars Tollen S Reagent Fehling S Solution Benedict S Solution - This allows the sugar to act as a reducing agent, for example in the maillard reducing sugars (monosaccharides, e.g.
Disaccharides Definition Examples Easy Biology Class. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides. In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Here are some common examples of reducing sugars. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of benedict's or fehling solution to cuprous ions.
Carbohydrates Intro : I Fail To See Carbonyl Group Here, How Can I Identify.
Reducing Non Reducing Sugars Tollen S Reagent Fehling S Solution Benedict S Solution. Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. Here are some common examples of reducing sugars. In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of benedict's or fehling solution to cuprous ions.
Chemistry Glossary Search Results For Maltose - A Reducing Sugar Is Any Sugar That Is Capable Of Acting As A Reducing Agent Because It Has A Free Aldehyde Group Or A Free Ketone Group.
What Are Reducing Sugars Master Organic Chemistry. Here are some common examples of reducing sugars. Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of benedict's or fehling solution to cuprous ions. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose.
Biology Exams 4 U Difference Between Reducing And Non Reducing Sugars : Examples Of Reducing Sugars Include Glucose, Fructose, Galactose As Monosaccharides And Lactose, Maltose As Disaccharides.
Reducing Sugar Wikipedia. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Here are some common examples of reducing sugars. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of benedict's or fehling solution to cuprous ions. In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides.
File - A Reducing Sugar Is Any Sugar That, In Basic Solution, Forms Some Aldehyde Or Ketone.
Which Of The Following Disaccharide Will Not Reduce Tollen S Reagent Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides. In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of benedict's or fehling solution to cuprous ions. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Here are some common examples of reducing sugars.
Pdf Food Sources And Analytical Approaches For Maltose Determination . A Reducing Sugar Is Any Sugar That Is Capable Of Acting As A Reducing Agent Because It Has A Free Aldehyde Group Or A Free Ketone Group.
Carbohydrates Monosaccharides Disaccharides Polysaccharides. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of benedict's or fehling solution to cuprous ions. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. Here are some common examples of reducing sugars. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides.
Reducing Sugar Wikipedia , To Be A Reducing Sugar, You Have To Have Either An Aldehyde Or A Ketone Functional Group.
The Structure Of Trehalose Trehalose Is A Non Reducing Disaccharide Download Scientific Diagram. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of benedict's or fehling solution to cuprous ions. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides. In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. Here are some common examples of reducing sugars. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides.
16 7 Disaccharides Chemistry Libretexts - I Fail To See Carbonyl Group Here, How Can I Identify.
10 Difference Between Reducing Sugar And Non Reducing Sugar With Examples Viva Differences. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of benedict's or fehling solution to cuprous ions. In basic aqueous media, nonreducing sugars do not generate any compounds containing an aldehyde. Some disaccharides, such as sucrose, are nonreducing sugars, meaning they cannot donate electrons to other molecules. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Disaccharides, the simplest polysaccharides, are the products of a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. Some disaccharides and all polysaccharides are reducing sugars. In other words, disaccharides are composed by 2 sugar molecules. Here are some common examples of reducing sugars. Examples of reducing sugars include glucose, fructose, galactose as monosaccharides and lactose, maltose as disaccharides. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: