Glucose Starch Glycogen And Cellulose Are Examples Of Which Macromolecule. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch: The solution of iodine in ki is used to detect a solution of starch and. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. Learn the importance of polysaccharides such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen along bakery products require starch for their elasticity, its examples would be cake and biscuit fillings. Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin. The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled. Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants. What are the 3 major polysaccharides?
Glucose Starch Glycogen And Cellulose Are Examples Of Which Macromolecule . Lipids C Nucleic Acids 4.
Ppt Complex Structures And Functions Of Carbohydrates Powerpoint Presentation Id 2170356. The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. What are the 3 major polysaccharides? Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants. Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin. Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. Learn the importance of polysaccharides such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen along bakery products require starch for their elasticity, its examples would be cake and biscuit fillings. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. The solution of iodine in ki is used to detect a solution of starch and. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch: Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled.
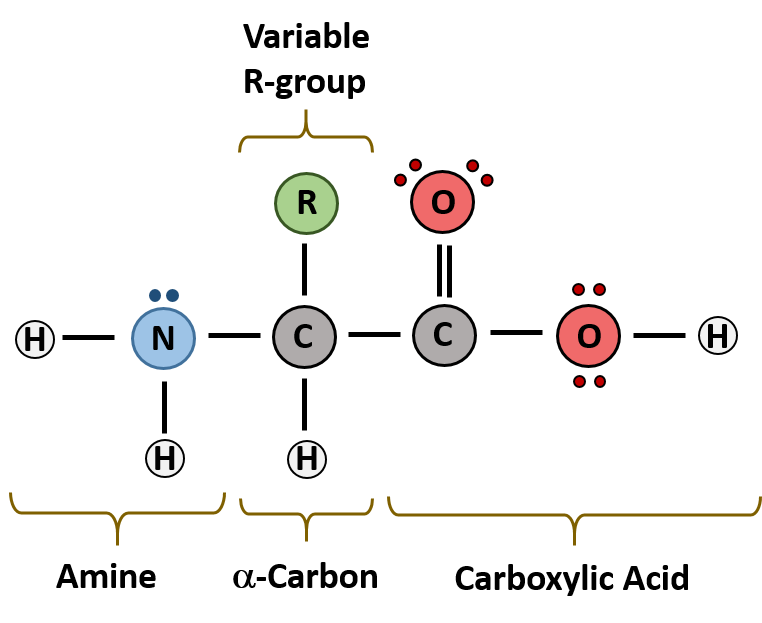
Monosaccharides and oligosaccharides are crystalline solids, soluble in water and sweet in taste.
Cellulose is a polysaccharide of beta glucose monomers, making every other glucose monomer upside down with respect to its neighbors. Examples include enzymes , antibodies, and muscle fiber. While polymers built with alpha glucose form helical. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch: Sugar, glucose , starch , glycogen , cellulose. Dna is an example of which macromolecule? Glucose, sucrose, starch, cellulose, chitin. Cellulose is also a string of glucose molecules. Fats, oils, waxes , steroids, phospholipids in membranes. Cellulose is important as they. Lipids c nucleic acids 4. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are examples of polysaccharides. Cellulose is a polysaccharide of beta glucose monomers, making every other glucose monomer upside down with respect to its neighbors. The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. Cellulose differs from starch and glycogen as it has a straight, unbranched chain instead of a coiled chain. Every other glucose monomer in cellulose is flipped over and packed tightly as extended long chains. That are used by living things as a source of energy. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. Apart from this, the major difference between the large numbers of hydrogen bonds still strengthen the cellulose, hence why it is good for structural purposes. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. Monosaccharides and oligosaccharides are crystalline solids, soluble in water and sweet in taste. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. Starch is the carbohydrate reserve of plants which is the most important dietary source for higher animals, including man. The cause of macromolecules orientation and aggregation are intermolecular hydrogen bonds. With thanks to angel herráez for permission to use his model in this video. This gives cellulose its rigidity and high tensile strength—which is so important to plant cells. Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin. Cellulose (cellulose is a tough structural carbohydrate which is impossible to digest, unless you are a bacterium or a its a hydrolysis reaction (the water is needed to break the bond between the glucose and fructose that make up the sucrose) Cellulose is a polysaccharide produced by plants. Apart from this, the major difference. What is the difference between starch and glycogen?
Structural Biochemistry Carbohydrates Polysaccharides Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World : While Polymers Built With Alpha Glucose Form Helical.
Biology Notes For A Level 16 Summary Of Biological Molecules. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch: What are the 3 major polysaccharides? Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. The solution of iodine in ki is used to detect a solution of starch and. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled. Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants. Learn the importance of polysaccharides such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen along bakery products require starch for their elasticity, its examples would be cake and biscuit fillings. Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin.
Macromolecules Worksheet 2 - What Are The 3 Major Polysaccharides?
Carbohydrates Sugars Starch Glycogen Cellulose Chitin Ppt Download. This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch:
Macromolecules Biology 1 With Papagiannis At Irvine Valley College Studyblue . Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants.
Biol2060 Cell Biology. Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin. In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. The solution of iodine in ki is used to detect a solution of starch and. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. Learn the importance of polysaccharides such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen along bakery products require starch for their elasticity, its examples would be cake and biscuit fillings. The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. What are the 3 major polysaccharides? Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled. Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch: This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose.
Biology Notes For A Level 16 Summary Of Biological Molecules : For Example, A Carbohydrate Is A Macromolecule That Is Classified As A Polymer Because It Is Made Up Of Repeating Monosaccharides, But A Fat (Lipid) Is A Macromolecule That Cannot Be Further Classified Because If You Look Under The 'Monomers' Column, It.
Carbohydrates. Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled. This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. What are the 3 major polysaccharides? Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. Learn the importance of polysaccharides such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen along bakery products require starch for their elasticity, its examples would be cake and biscuit fillings. The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch: The solution of iodine in ki is used to detect a solution of starch and.
Biological Macromolecules Enzyme Ppt Download : Sugar, Glucose , Starch , Glycogen , Cellulose.
Macromolecule Poster Project Acids Biology Carbohydrates Chemistry En Lipids Macromolecule Nucleic Nutrition Poster Glogster Edu Interactive Multimedia Posters. What are the 3 major polysaccharides? The solution of iodine in ki is used to detect a solution of starch and. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled. Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch: The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. Learn the importance of polysaccharides such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen along bakery products require starch for their elasticity, its examples would be cake and biscuit fillings. This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin.
Complex Carbohydrates Are Polysaccharides Expii : Glycogen Is Even More Readily Hydrolysed To A Glucose Due To The Short Chains.
Lecture Notes Lectures 3 4 Structure And Function Of Large Biological Macromolecules Studocu. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. Learn the importance of polysaccharides such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen along bakery products require starch for their elasticity, its examples would be cake and biscuit fillings. The solution of iodine in ki is used to detect a solution of starch and. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled. What are the 3 major polysaccharides? This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch: Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants.
Sugars Alimentarium - Fats, Oils, Waxes , Steroids, Phospholipids In Membranes.
Master Frameset. Learn the importance of polysaccharides such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen along bakery products require starch for their elasticity, its examples would be cake and biscuit fillings. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch: Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. What are the 3 major polysaccharides? In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled. Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin. This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants. Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. The solution of iodine in ki is used to detect a solution of starch and.
Intro Bio Lec 3 Columbia University : Cellulose Is An Important Structural Element Of The Cell Walls Of All Photosynthetic Plants.
Ch 3 Biological Macromolecules Flashcards Quizlet. Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants. What are the 3 major polysaccharides? Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. Learn the importance of polysaccharides such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen along bakery products require starch for their elasticity, its examples would be cake and biscuit fillings. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. The solution of iodine in ki is used to detect a solution of starch and. The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin. This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch:
Solved 1 Which Of These Is Not Considered To Be A Macrom Chegg Com : Glycogen, Starch, And Cellulose Are All Composed Entirely Of Glucose Residues, Which Cellulose , In Contrast, Has A Quite Distinct Function As The Principal Structural Component Of The Plant Cell Wall.
Organic Compounds Ck 12 Foundation. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. What are the 3 major polysaccharides? Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch: Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants. The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. The solution of iodine in ki is used to detect a solution of starch and. Learn the importance of polysaccharides such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen along bakery products require starch for their elasticity, its examples would be cake and biscuit fillings. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin.
Polysaccharides Biological Macromolecules : Starch, Glycogen And Cellulose Are All Polymers Of Glucose.
Metabolism The Synthesis Of Macromolecules Britannica. Nucleic acid is another type of macromolecule different examples are cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide. Autotrophs produce glucose as the simple sugar during starch: The simplest saccharide is glucose, a monosaccharide, c6h12o6.starch and cellulose are polysaccharides. In a glycogen molecule, the branching happens more frequently, almost after every six glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural element of the cell walls of all photosynthetic plants. Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates found in living cells. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. What are the 3 major polysaccharides? Starch is an example of biological macromolecule carbohydrate. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides. The solution of iodine in ki is used to detect a solution of starch and. Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled. This is one of the most abundant organic substances that are present in the plant kingdom. Learn the importance of polysaccharides such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen along bakery products require starch for their elasticity, its examples would be cake and biscuit fillings.