Examples Of Reducing Sugars. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: A reducing sugar is a chemical term for a sugar that acts as a reducing agent and can donate electrons to another molecule. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars. Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. Consider the reaction between an. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution.
Examples Of Reducing Sugars . Examples Of Reducing Sugars Include Glucose, Fructose, Galactose As Monosaccharides And Lactose.
Reducing And Non Reducing Sugars Test Ppt Download. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: Consider the reaction between an. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars. A reducing sugar is a chemical term for a sugar that acts as a reducing agent and can donate electrons to another molecule. Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides.
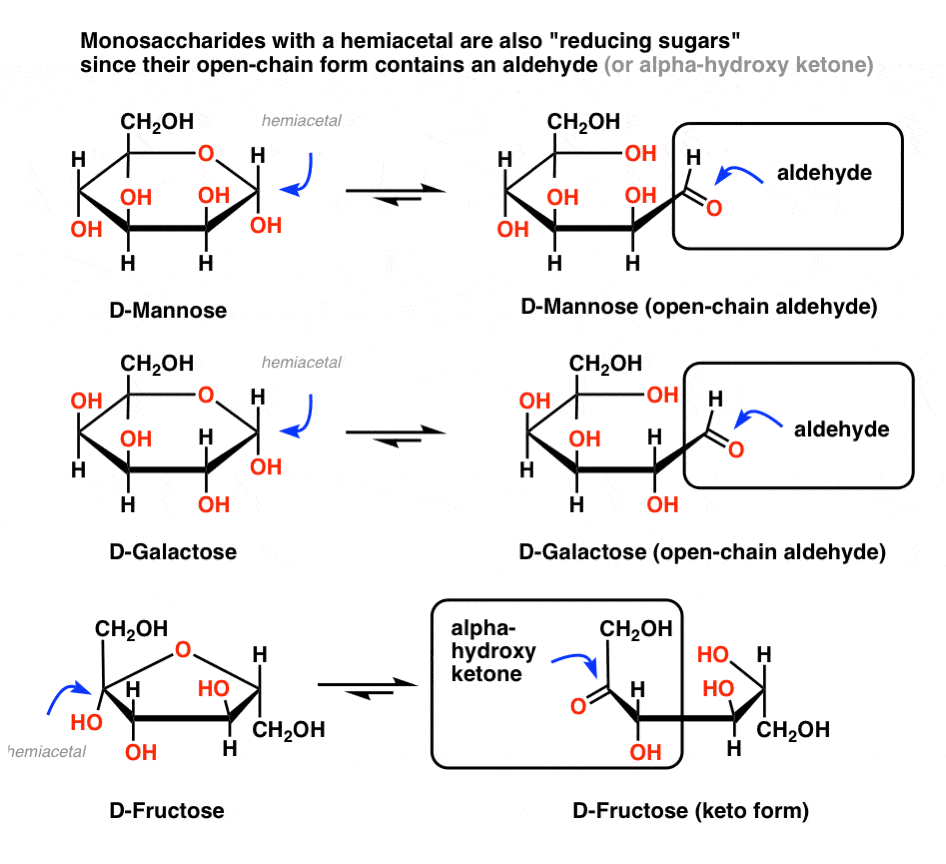
This allows the sugar to act as a reducing agent, for example a reducing sugar occurs when its anomeric carbon is free.
A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Note that the disaccharide sucrose is not a reducing sugar. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. It is a carbonyl in disguise), identification of reducing sugars becomes easier. Since sugars occur in a chain as well as a ring structure, it is possible to have an equilibrium. Free learning resources for students covering all major areas of biology. Fructose is the sweetest of the common natural sugars. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. Reducing sugar in the largest biology dictionary online. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. In aqueous medium, reducing sugars generate one or more compounds containing this is a characteristics property of reducing sugars. Sugar can be safely reduced by about a third without seeing many negative consequences. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: Two monosaccharides bond together with a glycosidic bond and form a disaccharide. Sugar is a type of carbohydrate found in both food and beverages. A reducing sugar is a carbohydrate that is oxidized by a weak oxidizing agent (an oxidizing agent capable of oxidizing aldehydes but not alcohols, such as the tollen's reagent) in basic aqueous solution. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Reducing sugars readily interact with amino acids and give rise to maillard reaction products, which lead to progressive browning and aroma formation. A reducing sugar is any sugar that, in basic solution, forms some aldehyde or ketone. Reducing sugar is a saccharide that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde or ketone group. Aldehydes and keto groups have reducing character and reduce tollens reagent and fehling's (benedict's) solution. Definition noun a sugar that serves as a reducing agent due to its free aldehyde or ketone functional groups in its molecular structure. Monosaccharides » glucose, galactose, fructose 2. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Many fruits and vegetables contain this monosaccharide. Examples of added sugars that may be listed as an ingredient include: Once you realize that a hemiacetal can equilibrate with a carbonyl (e.g. Reducing sugars can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution.
19 Analysis Of The Sugars In Soft Drinks , It Is A Carbonyl In Disguise), Identification Of Reducing Sugars Becomes Easier.
Reducing Sugar Baking Ingredients Bakerpedia. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests. A reducing sugar is a chemical term for a sugar that acts as a reducing agent and can donate electrons to another molecule. Consider the reaction between an. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides. Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose.
Carbohydrates . The Most Important Monosaccharide And Reducing Sugar Is Glucose.
Testing For Saccharides Ppt Video Online Download. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. Consider the reaction between an. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars.
Food Tests Benedict S Test For Reducing Sugar Brilliant Biology Student . Definition noun a sugar that serves as a reducing agent due to its free aldehyde or ketone functional groups in its molecular structure.
Properties Of Disaccharides A Level Biology Revision Notes. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution. A reducing sugar is a chemical term for a sugar that acts as a reducing agent and can donate electrons to another molecule. Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. Consider the reaction between an. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel:
Bio Chapter 4 Spm - Examples Of Reducing Disaccharides Are Lactose And Maltose.
Why Is Glucose Called A Reducing Sugar Quora. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. A reducing sugar is a chemical term for a sugar that acts as a reducing agent and can donate electrons to another molecule. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Consider the reaction between an. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides.
Reducing Sugars Are Identified By Brainly In - Examples Of Reducing Disaccharides Are Lactose And Maltose.
Plos One Public Acceptability In The Uk And Usa Of Nudging To Reduce Obesity The Example Of Reducing Sugar Sweetened Beverages Consumption. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution. The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. A reducing sugar is a chemical term for a sugar that acts as a reducing agent and can donate electrons to another molecule. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. Consider the reaction between an. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests.
Fehling S Solution Definition Example And Mechanism , It's The Other Issues That Arise That.
Reducing And Non Reducing Sugars Test Ppt Download. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: A reducing sugar is a chemical term for a sugar that acts as a reducing agent and can donate electrons to another molecule. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests. Consider the reaction between an. Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides.
Food Tests Benedict S Test For Reducing Sugar Brilliant Biology Student , Once You Realize That A Hemiacetal Can Equilibrate With A Carbonyl (E.g.
Benedict S Test Definition Principle Uses And Reagent. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution. Consider the reaction between an. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests. A reducing sugar is a chemical term for a sugar that acts as a reducing agent and can donate electrons to another molecule. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides.
Di And Polysaccharides , Examples Include Glucose, Fructose, Maltose And.
Learn Reducing And Non Reducing Sugars In 3 Minutes. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. Consider the reaction between an. Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. A reducing sugar is a chemical term for a sugar that acts as a reducing agent and can donate electrons to another molecule. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests.
Incentives And Disincentives For Reducing Sugar In Manufactured Foods . Anhydrous Dextrose, Agave, Barley Malt, Beet Sugar, Brown Rice Syrup, Brown Sugar, Cane Juice, Cane Sugar, Cane Syrup, Coconut Palm Sugar, Concentrated Fruit Juice, Confectioner's Sugar, Corn Sweetener, Corn Sugar, Corn Syrup.
What Are Reducing Sugars Master Organic Chemistry. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. A reducing sugar is a chemical term for a sugar that acts as a reducing agent and can donate electrons to another molecule. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. Consider the reaction between an. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and. Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel:
Food Tests Benedict S Test For Reducing Sugar Brilliant Biology Student - Reducing Sugars Give A Dark Red Color (Brick Color) When They React With Benedict Solution.
What Are Five Examples Of Non Reducing Sugars Chemistry Question. The carbonyl group (c=o) in an aldose is readily oxidised to a carboxylate group glucose and galactose are both examples of aldose sugars. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce. The most important monosaccharide and reducing sugar is glucose. A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides. Mbd alchemie presents a video that talks about the classification of the carbohydrates as reducing and non reducing sugars subscribe to our channel: A reducing sugar is a chemical term for a sugar that acts as a reducing agent and can donate electrons to another molecule. Reducing sugars give a dark red color (brick color) when they react with benedict solution. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests. Consider the reaction between an. Common examples of polysaccharides are starch. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides, and some polysaccharides. Sugars are able to form long chains with each other in arrangements known as polysaccharides. Glucose and galactose can be oxidised by a mild oxidising agent. Examples include glucose, fructose, maltose and.